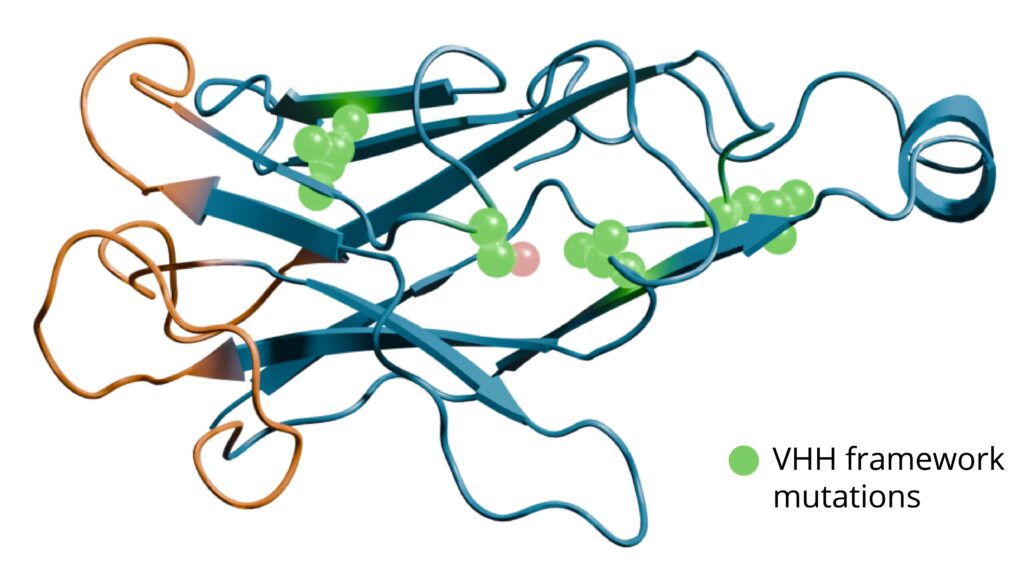
Engineering of single-domain antibodies
Rapid current developments in protein structure prediction, protein engineering, and protein design allow novel in silico approaches that were not feasible until recently as exemplified by the 2024 Nobel prize in chemistry. Moreover, novel DNA synthesis approaches allow rational design of tailored variant libraries which can be used to generate large amounts of VHH variants based on a lead sequence.
At QVQ, we can leverage our extensive experience in sdAb development, access to a wet lab, and phage display setup to suggest, produce and experimentally test in silico engineered sdAbs and/or sdAb libraries.
For example, (in silico) protein engineering approaches can be used for humanization of sdAbs, increasing their developability, inserting protein A binding affinity or enhancing the intrinsic enzymatic- and thermostability. Another common request is to enhance the binding affinity of a sdAb (a.k.a. affinity maturation).
The melting temperature (Tm) of an antibody is an important factor for its developability. A higher Tm value indicates better stability and therefore a lower risk for unfolding and aggregation. Stable antibodies are easier to manufacture, store, and use therapeutically, with longer shelf-life. Tm assessment and engineering at an early stage minimizes late-stage development failures. QVQ can experimentally validate improved thermal stability by Thermal Shift Assays (TSA) or Differential Scanning Fluorimetry (DSF) and generate stability-enhanced variants of your lead sdAb.
Both experimental and in silico engineering approaches can be used in isolation or combined to rationally introduce mutations to improve the binding affinity.
We offer bespoke solutions for your project and provide a realistic picture of which engineering approaches are possible, feasible and could be applied by QVQ.