Cell-based assays
QVQ offers the following cell-based characterizations of sdAb functionality. These can be applied to measure functional effects of purified sdAbs to evaluate agonism and antagonism as well as potencies and efficacies. Some of these can also be applied to crude periplasmic extracts for screening purposes.
Target pharmacology
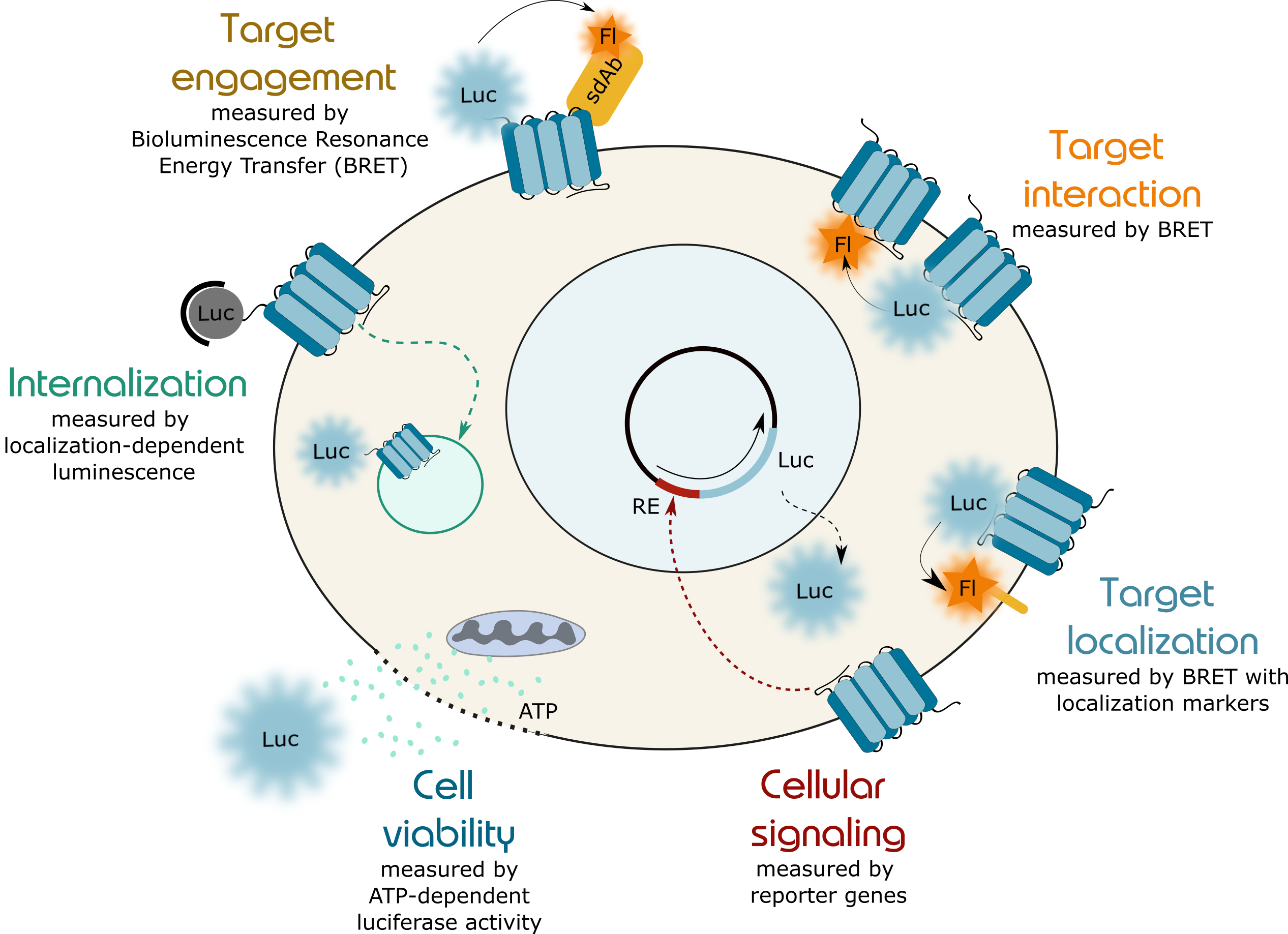
- Target engagement
- Protein-protein interactions (target dimerization, target-effector interaction)
- Target localization
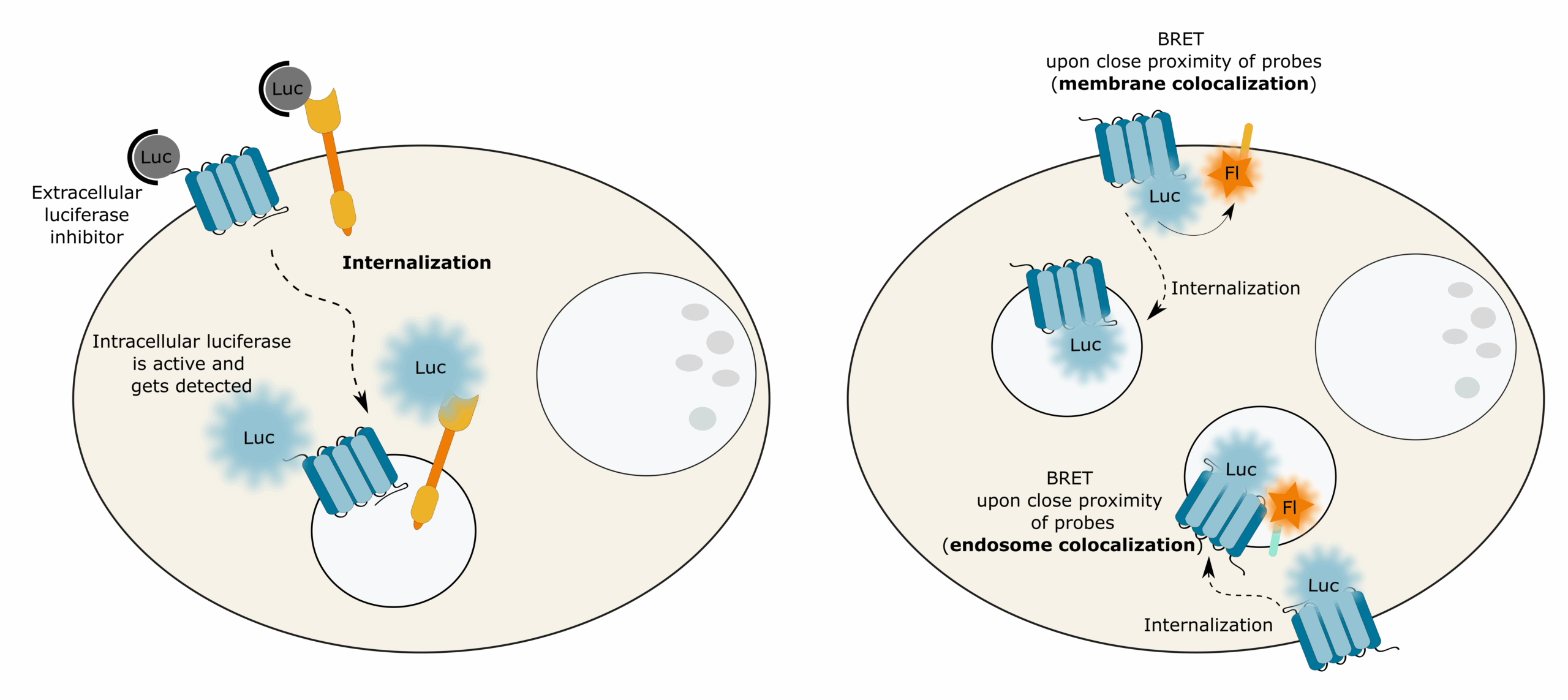
- Target internalization
Cellular Responses
- Cell viability
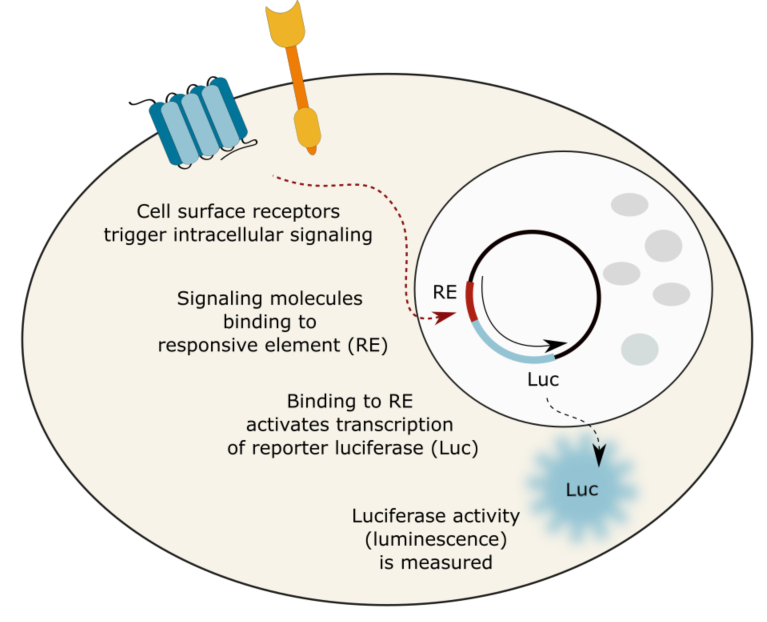
- Cellular signaling (AP1, cAMP, NF-κB, NFAT, ERK/MAPK, G12/RhoA, Wnt/β-catenin)
- Immune cell activation (ADCC, ADCP)
More information about the different assays is listed below.
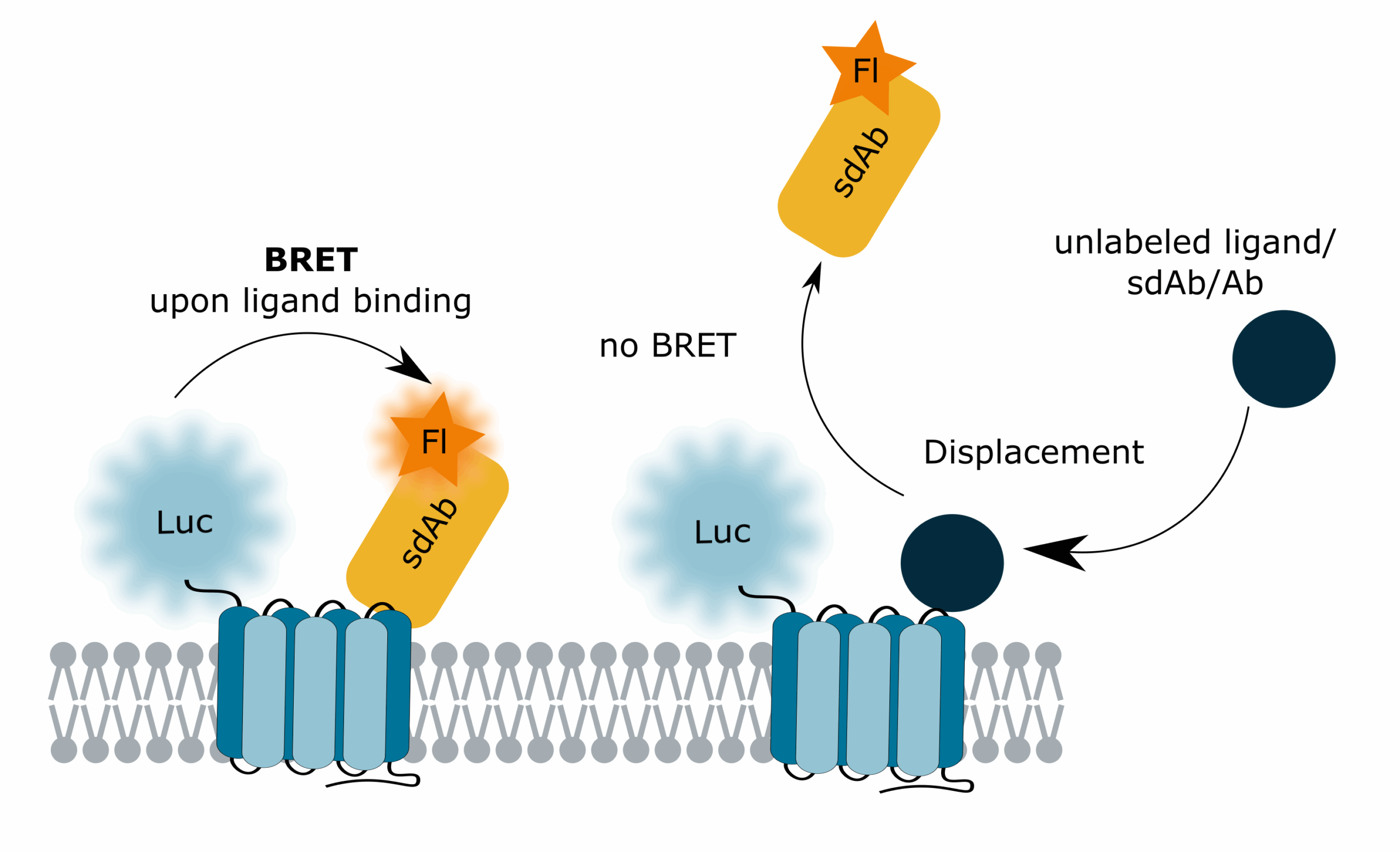
Target engagement
Binding of sdAbs can be measured with nanometer resolution using Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET) assays.
Target proteins are fused to luciferases and transiently transfected into mammalian cells (e.g., HEK293T). Live cells or membrane extracts are exposed to fluorescent sdAbs. Upon sdAb binding, the fluorophore is excited via energy transferred from the luciferase. This energy transfer only occurs in nanometer distance (<10 nm) allowing for the measurement of true target engagement in a one-step, no-wash assay.
This assay format also allows for the measurement of unlabeled probes in displacement assays and by conformational sensing.
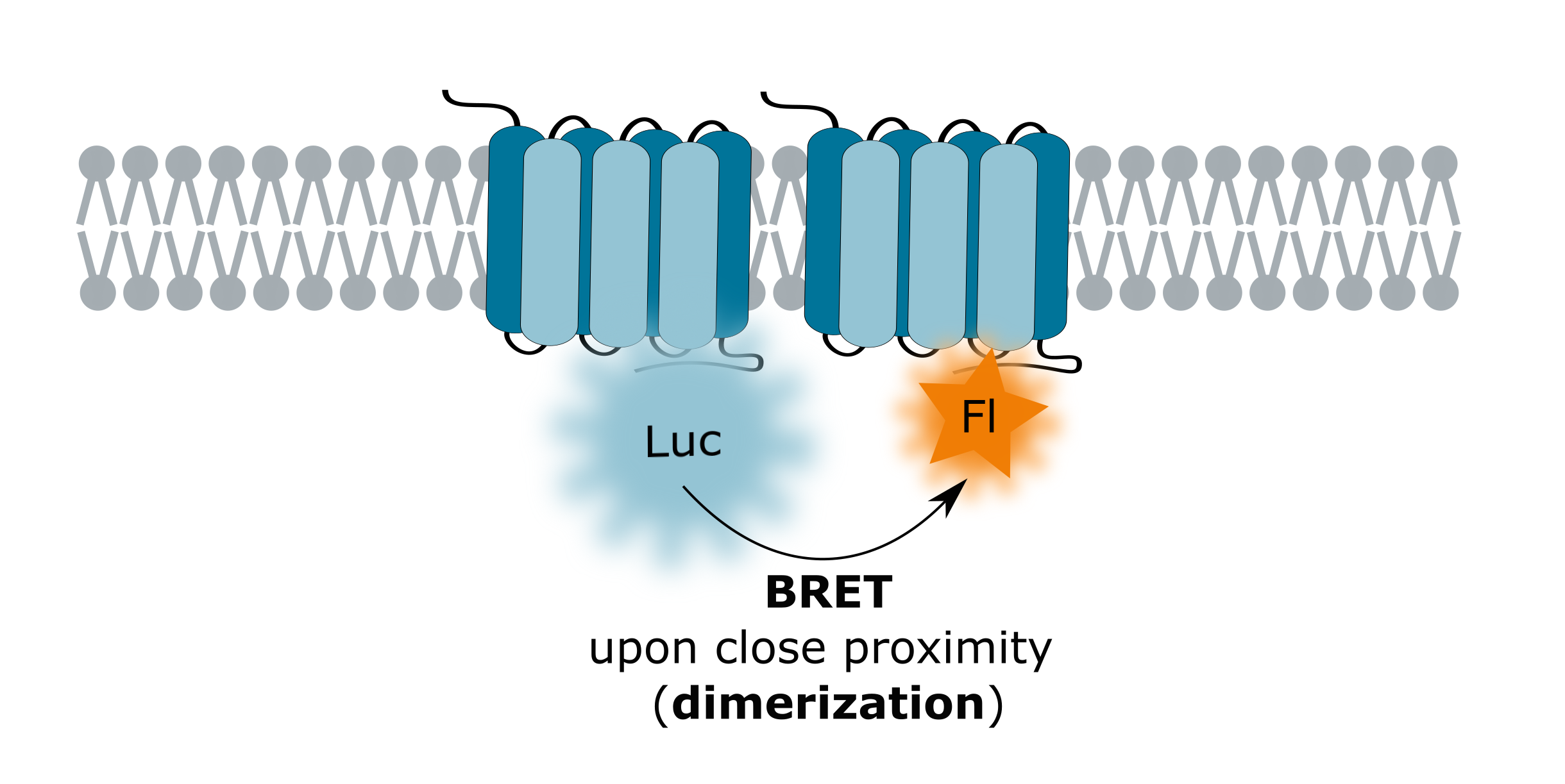
Protein-protein interaction
Protein-protein interactions, such as target dimerization, can be measured using BRET between engineered receptors.
Target proteins are fused to a luciferase and fluorophore and transiently transfected into mammalian cells (e.g., HEK293T).
Binding of sdAbs can be measured with nanometer resolution using Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET) assays. Modulators such as sdAbs can be added to measure their effect on the dimerization. The high resolution of BRET (<10 nm) allows for sensitive detection small-scale interactions such as GPCR dimers only a few nanometers in size.
Target localization and internalization
Localization of target proteins within live cells – and the modulatory effect of sdAbs on this – can be measured by BRET assays or by location-dependent luciferase activity.
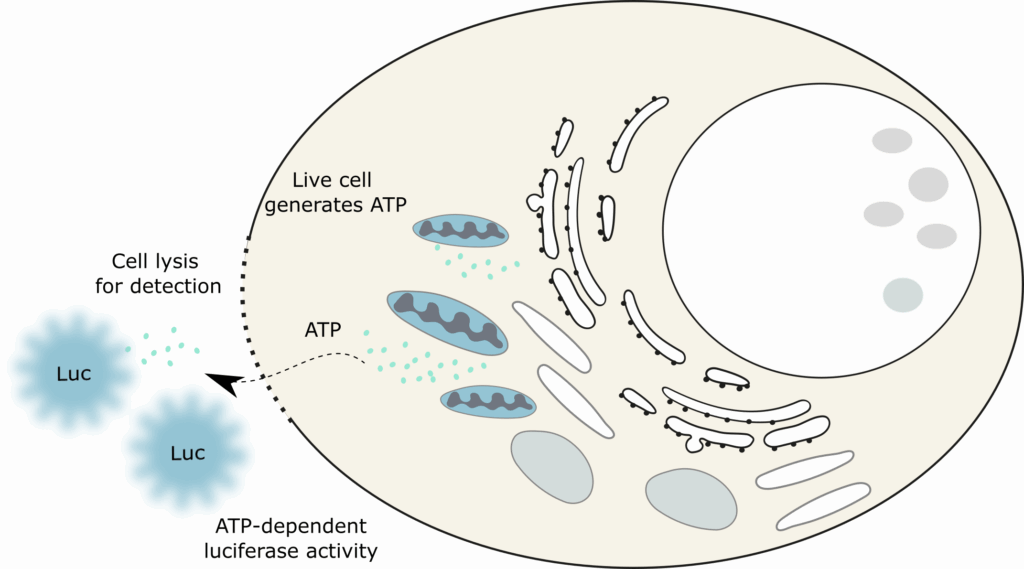
Cell viability
Cell viability can be measured by the ATP generated by live cells. ATP is a crucial cofactor for the luciferase utilized in this assay. Therefore, the lumininescence directly correlates to the amount of ATP and to the amount of live cells.
Cellular signaling
Modulation of cellular signaling can be measured via luminescent reporter gene assays for the following signaling pathways:
- AP1
- cAMP
- NF-κB
- NFAT
- ERK/MAPK
- G12/RhoA
- Wnt/β-catenin
In a similar way, activation of immune cells can be measured in ADCC and ADCP assays via NFAT and THP-1 reporter assays, respectively.