25 January 2023
Candida albicans is an opportunistic yeast naturally occurring on our body. This yeast can become pathogenic causing candidiasis. Candidalysin, a peptide toxin secreted by the fungus, is involved in Candida becoming pathogenic the mediates its translocation through intestinal epithelium causing serious infections.
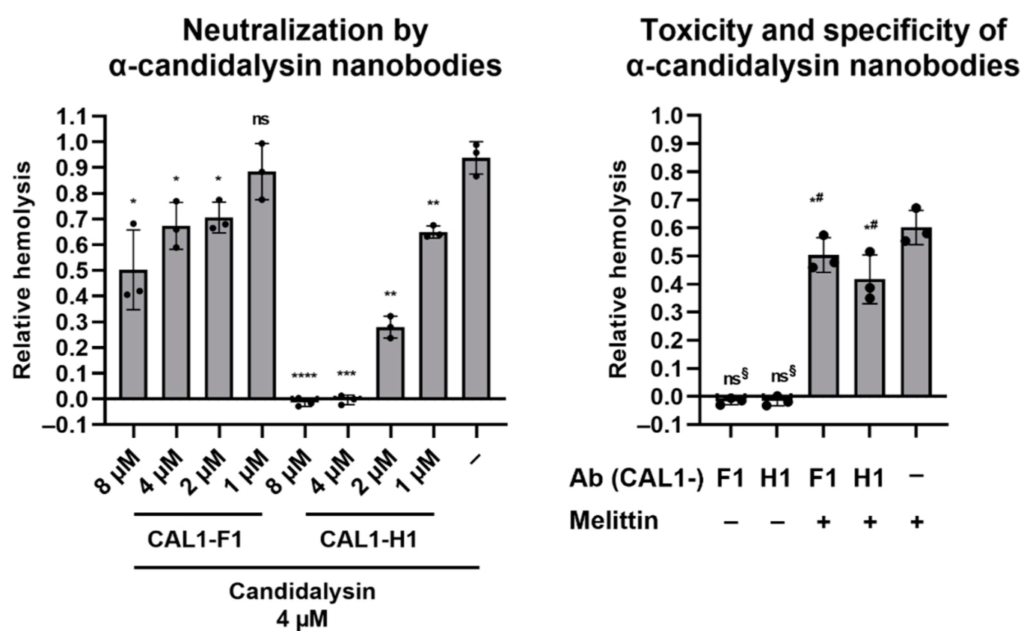
A recent study led by prof. Bernard Hube now shows that Candidalysin is also the driver of C. albicans-associated haemolysis. This process can be fully inhibited by two single domain antibodies.